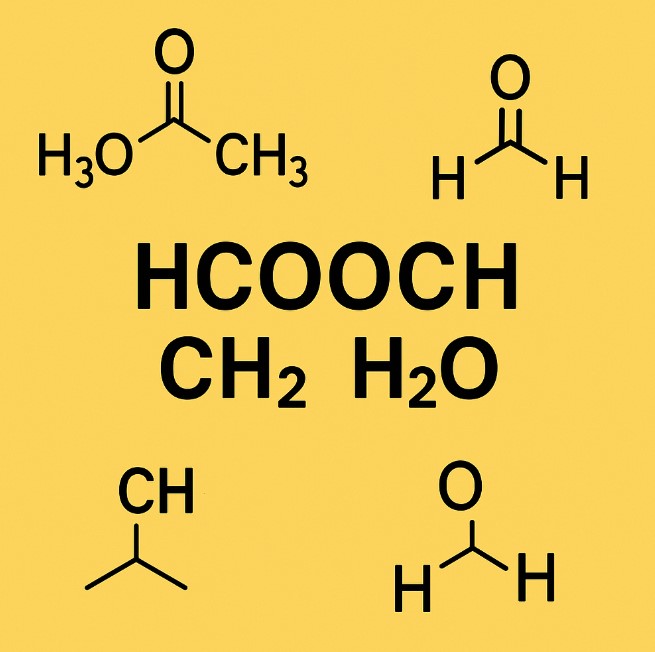
Understanding HCOOCH CH₂ H₂O: Structure, Reactions, and Applications
In chemistry, even simple-looking formulas can open the door to very important reactions and materials. One such combination is HCOOCH CH₂ H₂O, which includes formate esters, methylene groups, and water. Though this formula looks complex at first, it involves well-known organic components that play a vital role in labs, industries, and even eco-friendly solutions.
Let’s explore what HCOOCH CH₂ H₂O means, how it reacts, and where it is used.
What Does HCOOCH CH₂ H₂O Represent?
To understand this chemical group, we can break it down into parts:
-
HCOOCH – This is a formate ester, commonly seen as methyl formate (HCOOCH₃), formed from formic acid (HCOOH) and an alcohol like methanol.
-
CH₂ – A methylene group, usually a bridge or link between molecules in organic chemistry.
-
H₂O – Water, which acts as a solvent or reactant in many reactions.
Together, these parts are often discussed in the context of organic reactions involving esterification, hydrolysis, and formylation.
Structure and Properties
| Component | Description |
|---|---|
| HCOOCH (Formate Ester) | Has a sweet smell; used in organic synthesis. |
| CH₂ (Methylene) | A reactive group often used as a linking unit. |
| H₂O (Water) | Common polar solvent; helps drive hydrolysis reactions. |
The formate ester part is slightly polar and reactive. When combined with water, it tends to undergo hydrolysis—breaking into formic acid and alcohol. The methylene group may come from reagents like formaldehyde or methylene chloride and is often part of reduction or formylation processes.
Key Reactions Involving HCOOCH CH₂ H₂O
Let’s look at some important reactions where this formula or its components are involved:
1. Hydrolysis of Methyl Formate
This is one of the most common reactions:
Water breaks down the ester into formic acid and methanol. This is important in lab-scale and industrial reactions.
2. Esterification Reaction
The reverse of hydrolysis:
Formic acid and methanol produce the ester, methyl formate, and water. This is an equilibrium reaction.
3. Formylation Using Methylene Groups
In some advanced organic synthesis reactions, methylene bridges are used to attach formyl (HCO–) groups to other molecules.
Applications of HCOOCH CH₂ H₂O Components
These chemicals are not just found in the lab but also serve useful purposes across various industries:
| Use Case | Description |
|---|---|
| Organic Synthesis | These chemicals act as starting materials for other compounds. |
| Polymer Production | Methylene and ester groups are used in plastics and resins. |
| Green Chemistry | Water-based reactions reduce need for toxic solvents. |
| Fuel Cells | Formic acid and esters are studied for hydrogen storage and fuel generation. |
Role in Green Chemistry
One of the best things about this combination is that it supports eco-friendly chemical processes. Since water is a natural solvent and formate esters are biodegradable, reactions involving HCOOCH CH₂ H₂O are often used in sustainable chemistry.
Advantages include:
-
Lower toxicity
-
Recyclable solvents
-
Fewer by-products
This makes it useful in environmentally conscious industries, especially those moving away from petroleum-based materials.
Physical and Chemical Characteristics
| Property | Formate Esters |
|---|---|
| Appearance | Clear, colorless liquid |
| Odor | Fruity, slightly pungent |
| Solubility | Soluble in water and alcohol |
| Boiling Point | Around 32–45°C (depends on the ester) |
These properties make formate esters useful in perfumes, coatings, and flavoring agents in small quantities.
Safety and Handling
While the individual components are generally low-risk, caution is always advised:
-
Formate esters are flammable.
-
Formic acid, if formed during hydrolysis, can be corrosive.
-
Water makes the reaction easier but must be pure for lab work.
Proper ventilation, gloves, and goggles are recommended during handling.
“This makes it useful in environmentally conscious industries, especially those moving away from petroleum-based materials. Platforms like [Quartist] also focus on sustainable research and green innovations in science.”
Summary Table
| Feature | Detail |
|---|---|
| Main Compound | HCOOCH CH₂ H₂O |
| Functional Groups | Ester, methylene, water |
| Common Reactions | Hydrolysis, esterification, formylation |
| Industrial Use | Fuel cells, organic synthesis, resins |
| Environmental Benefit | Green chemistry, recyclable solvents |
Conclusion
The combination of HCOOCH CH₂ H₂O may seem like a niche chemical formula, but it stands for much more in the world of chemistry. It connects vital organic groups used in daily chemical industries—from plastics and fuels to perfumes and lab reagents.
Its ability to react easily in water, along with its natural origin and biodegradability, makes it an important player in the shift toward green and sustainable chemistry.
Understanding the roles of its components—formate esters, methylene bridges, and water—helps us see how even small molecules shape big scientific solutions.